SUNSAT
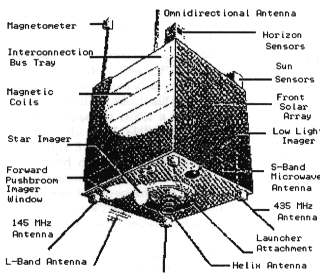
SUNSAT is a new experimental satellite under construction by students
at the University of Stellenbosch, South Africa. This satellite
is similar to the UoSATs built by the University of Surrey. SUNSAT
is a microsatellite-class spacecraft that will be launched in
January 1996 by NASA from Vandenberg Air Force Base on an Air
Force Delta II as a replacement counter weight for the Danish
Oersted microsatellite.
SUNSAT's primary payload is an amateur radio communications system
that will support VHF, UHF, and S/L-bad links, a 9600 baud packet
radio bulletin board system, a high-resolution imager, and some
innovative communication packages and experiments:
- Parrot system on the 2-meter band that will relay approximately
8 seconds of speech
- 2-meter analog channel for voice storage and transponder use
- 24-cm/13-cm linear transponder that will be available for
experimenters and repeating television signals
- Bulletin board system that will enable the satellite to store
files and other information in a "mailbox"
- 2-meter 1200 baud AFSK-FM packet radio transponder compatible
with terrestrial VHF-FM packet radio stations
- 2-meter/70-cm 9600 FSK (frequency shift keying) baud digital
store-and-forward transponder
- CCD star Camera for accurately determining the satellite's
attitude relative to the stars
- Tri-band (color) CCD imager with a resolution of 15-meters
per pixel
SUNSAT Characteristics:
- COSPAR ID: TBD
- Launch Date: early 1996
- Launch Vehicle: U.S. Air Force Delta II rocket
- Reflectors:
- Shape (array):
- Size: 45cm x 45cm x 40cm
- Orbit: elliptical polar orbit
- Inclination: 98.6 degrees
- Altitude: 400 km to 840 km (guarantee 15 min. access time
to any ground station on the globe)
- Period: 100 min.
- Weight: 50 kg
Source: Magliacane, John A. "Amateur Radios Satellites",
Satellite Times, Vol. 1, No. 5, May/June 1995.

